Background: Recent approval of ruxolitinib (rux) for steroid refractory graft versus host disease (GvHD) has revolutionized the field and provided tremendous choice for the patients. However, the side effects including thrombocytopenia leads to dug discontinuation and intolerance. We have previously shown that adoptive therapy with cord blood (CB) derived T regulatory (Treg) cells can prevent and treat GvHD. We hypothesized that the addition of CB Treg therapy to rux based therapy can augment overall efficacy.
Methods: CellTrace Violet suppression assay was performed to evaluate the suppressor function of CB Treg cells in the presence or absence of rux. Xenogenic GvHD mouse model was utilized where the NSG mice underwent sublethal irradiation on day -1 followed by injection of 1x107 donor peripheral blood (PB) mononuclear cells (MNCs) on day 0. Oral rux at 1 mg daily was fed continuously to the mice in the presence or absence of 1x107 CB Treg cells, tagged with CellTrace Violet dye, administered on days +4, +7, +11, +18. Mice were followed every other day for weight, GvHD score and survival. Serial blood draws were performed to analyze for cell compartment and cytokine assays.
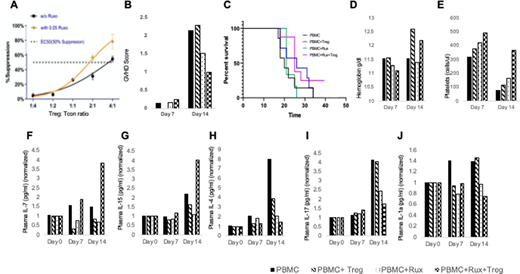
Results: We examine whether the addition of rux impacts the suppressor function of CB Treg cells. Varying concentration of rux including 0.01, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.5 µM were added at 24, 48 and 96 hours of the cell suppression assay. The addition of rux 0.05 µM at 48 hours of the cell suppression culture led to a restoration of poor cell function (Figure A). Lowest GVHD score was reported in the rux+CB Treg combination arms at day +14 when compared to rux alone or CB Treg alone arm which (Figure B) translated into a superior survival in the rux +CB Treg arm (Figure C). Furthermore, an increase in the hemoglobin level (Figure D) and the platelet count (Figure E) was demonstrated in the rux+CB Treg arm.
Addition of rux led to longer persistence of the injected CB Treg cells on day 14 (data not shown) which correlated with the increase in the plasma level of the pro-Treg cell signaling markers including IL-7 (Figure F) and IL-15 (Figure G). A decrease in the IL-4 production supported the increased Treg cell function (Figure H). A synergistic suppression of inflammatory cytokines including IL-17 (Figure I) and IL1A (Figure J) was evident in the rux+CB Treg arm.
Conclusion: The combination of CB Tregs with ruxolitinib leads to improved overall survival, decreased inflammatory cytokines and improved hematologic parameters. Such combination should be explored in a clinical setting
Sadeghi:Cellenkos Inc.: Current Employment. Parmar:Cellenkos Inc.: Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal